About The Author: Travis Baugh is a Digital Brand Marketing Manager for Bryant, where he creates clear, helpful content to guide homeowners through heating, cooling, and indoor air quality decisions. His goal is to empower readers with the knowledge they need to choose the right comfort solutions for their home—confidently and comfortably.
What Are the Main Types of Heat Pump Systems?
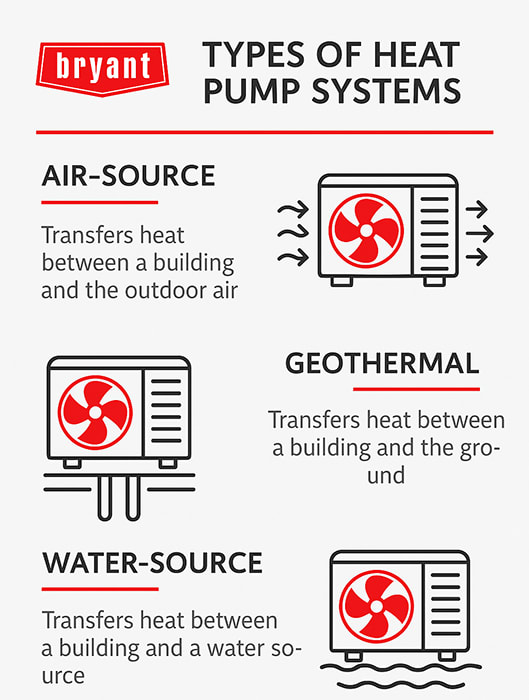
The three main types of heat pump systems are air-source, geothermal (ground-source), and air-to-water. Each system is designed to transfer heat rather than generate it, providing an energy-efficient solution for year-round heating and cooling tailored to different climates and home layouts.
Heat pump systems represent a cornerstone of modern, energy-efficient home comfort. By understanding the differences between these systems—including ducted and ductless configurations—you can make a confident investment in your home’s long-term value and comfort.
How Do Heat Pump Systems Work?
Heat pumps maintain comfortable indoor temperatures by moving heat instead of creating it through combustion. A refrigerant circulates through the system to absorb heat from an external source—such as the air, ground, or water—and releases it inside your home. This process is fully reversible, allowing the system to cool your home in summer by moving indoor heat outside.
Because they move heat rather than burn fuel, heat pumps deliver significantly more energy than they consume. This leads to a smaller carbon footprint and "efficiency that pays for itself" through lower utility bills.
Modern advancements have also introduced cold climate heat pumps, engineered to provide reliable warmth even when outdoor temperatures drop significantly. Learn more about what is a heat pump and how heat pumps work..
What Are the Three Main Types of Heat Pumps?
Heat pumps are categorized by their heat source. The three primary types are air-source, ground-source (geothermal), and water-source, each offering unique benefits for residential heating and cooling.
Air-source heat pumps
Air-source heat pumps are the most common type used in homes today. They operate by extracting heat from the outside air and transferring it indoors. This process works even in cold weather, as a specialized refrigerant absorbs ambient heat and circulates it through the system.
Key Benefits of Air-Source Heat Pumps:
- Energy Efficiency: They can produce up to three times more heat energy than the electrical energy they consume.
- Easier Installation: Compared to other systems, they are simpler and quicker to install, requiring less space.
- Adaptability: Their versatility makes them a popular choice for a wide range of climates and homes.
Geothermal (Ground-Source) Heat Pumps
Geothermal heat pumps leverage the stable temperature of the earth to heat and cool your home. A system of buried pipes circulates a fluid that absorbs heat from the ground in the winter and dissipates heat into it during the summer.
Key Benefits of Geothermal Heat Pumps:
- Exceptional Efficiency: These are among the most energy-efficient heating and cooling systems available, leading to major reductions in energy costs.
- Long Lifespan: Geothermal systems often last longer than air-source units due to the underground components being protected from the elements.
- Quiet Operation: They operate very quietly, enhancing home comfort.
Air-to-Water Heat Pumps
Air-to-water heat pumps are an innovative solution gaining popularity for homeowners seeking low-carbon alternatives to traditional boilers. These systems extract heat from the outside air and transfer it to water, which then circulates through hydronic distribution systems like radiators or in-floor radiant heating. Thanks to inverter technology, they offer strong performance in cold climates and are a key part of the electrification movement.
Understanding these main types of heat pump systems can assist homeowners in selecting the most appropriate option, ensuring year-round comfort and energy efficiency. Learn more about heat pump benefits.
What Is the Difference Between Ducted vs. Ductless Heat Pumps?
When selecting a heat pump, a crucial decision is whether to choose a ducted or ductless system. A ducted heat pump distributes conditioned air through a network of ducts, while a ductless mini-split system uses one outdoor unit connected to multiple indoor air handlers.
- Ducted Heat Pumps: These systems are ideal for homes that already have existing ductwork. They provide consistent, whole-home heating and cooling by delivering air to every room connected to the duct system. If your home lacks ductwork, installation can be more involved and costly.
- Ductless Mini-Split Systems: Ductless mini-split systems offer exceptional flexibility. They consist of an outdoor unit linked to one or more indoor units mounted on walls or ceilings. This setup allows for zoned heating and cooling, meaning you can control the temperature of individual rooms independently. Installation is less invasive, requiring only a small hole in the wall.
Ductless systems often provide greater energy efficiency because they avoid the energy losses that can occur through ductwork, helping to lower your heating and cooling bills.
How Do I Choose the Right Heat Pump for My Home?
Selecting the optimal system requires balancing your local climate, home structure, and efficiency goals. While an HVAC professional can provide a precise load calculation, consider these factors:
- Your Local Climate: While heat pumps have always been excellent for moderate climates, new cold climate models perform efficiently even in freezing temperatures, making them a viable option for colder regions.
- The Size of Your Home: A system that is too small will run constantly, while one that is too large will cycle on and off too frequently. An HVAC professional should perform a load calculation to determine the correct size for your home.
- Your Home’s Insulation: A well-insulated home retains heat more effectively, maximizing your heat pump's efficiency and reducing energy bills. Consider upgrading your insulation before installing a new system.
- Energy Efficiency Ratings: Look for high SEER2 (Seasonal Energy Efficiency Ratio) and HSPF2 (Heating Seasonal Performance Factor) ratings. Higher ratings mean greater efficiency and lower operating costs over the life of the unit.

Connect With A Bryant Dealer Today
Choosing the right heat pump is a pivotal decision that impacts your home's comfort, energy bills, and environmental footprint for years to come. At Bryant, we offer a complete range of innovative heat pump systems designed for superior performance and reliability.
Your local Bryant dealer has the expertise to guide you to the perfect solution for your home. Schedule an appointment today to get a quote for heat pump cost and ensure you invest in a system that delivers optimal comfort and efficiency.
Discover Bryant Heat Pumps
Choose a Bryant high efficiency heat pump for reliable, energy-efficient heating and cooling all year round. Known for their durability and advanced technology, Bryant heat pumps offer superior comfort while lowering energy costs. With quiet operation and smart features like variable-speed motors, Bryant systems ensure optimal temperature control. Backed by industry-leading warranties and professional heat pump installation from your local Bryant dealer, a Bryant heat pump is a long-term investment in comfort, efficiency, and peace of mind for your home.
Learn More About Heat Pumps
- Discover the differences between a heat pump vs furnace
- Understand what is an electric heat pump
- Discover what is auxiliary heat
- Learn about heat pump maintenance
- Find out more about heat pump replacement
- Read up on dual fuel heat pumps



